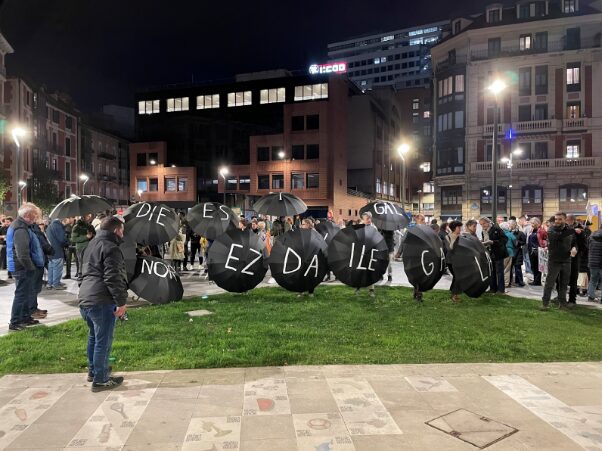Taking Action With Emmaüs
Regularisation of undocumented migrants in Spain: 500,000 reasons for Emmaus to celebrate!
On 27 January the Spanish government approved a decree to regularise over 500,000 undocumented migrants. This political decision came in the wake of a citizen campaign in which Emmaus Spain was heavily involved.
The account provided by Rosa Gil, the leader of Emmaus Bilbao, gives us all hope:
The Emmaus groups in Spain are celebrating. A civic legislative proposal calling for the exceptional regularisation of hundreds of thousands of migrants has been adopted. We can draw a key lesson from this collective campaign, in which we played an active part: local community organisations are capable of transforming reality and opening up gaps in systems that had previously seemed unbreachable.
The struggle got underway in 2020 when over 120 civil society organisations sent a letter to the Spanish government calling for an urgent and exceptional regularisation. At the time, it was estimated that close to 800,000 people were surviving in Spain without fundamental rights, and were trapped by their irregular administrative status. Hundreds of people protested outside the Spanish Parliament to call for a debate. However, the proposal was rejected in September of that year. Even the Socialist Party, which was already in power, made use of the European Pact on Migration and Asylum to vote against the proposal.
Far from giving up, the Regularización Ya (Regularise Now!) platform turned to the European Parliament; it confirmed that there were no legal barriers to such a measure being implemented. The next step was to arrange meetings in 2021 to launch a civic legislative proposal. This wasn’t an easy process: the proposal was rejected on several occasions until December 2021, when the official collection of signatures began. A national campaign was launched in January 2022. The campaign mobilised hundreds of collectives and volunteers. At the same time, over 80 motions of support were endorsed by local councils and the Basque Parliament.
Over 700,000 signatures were handed to the Spanish Parliament in December 2022, well over the minimum required level of 500,000. Finally, in April 2024, the civic legislative proposal was placed on the parliamentary agenda, with 310 votes for, and 33 against, the latter being cast by the far right. Following months of political deadlock, the initiative finally came to fruition thanks to pressure from Podemos, a small yet highly combative political party.
It is true that there was political will once we reached the home straight, including from the incumbent socialist government, but none of this would have been possible without social pressure. At a historic time when fascism, racism and indifference to human suffering are all gaining ground, the grassroots community movement demonstrated its transforming power.
We are celebrating today, but we are also making a new commitment: informing, supporting and making all of our resources available to this regularisation process so that nobody is left on the sidelines. Solidarity and the defence of human rights are upheld through collective effort. Only together can we counteract the discourse that is trying to make us forget that at some point in time, we were all migrants.
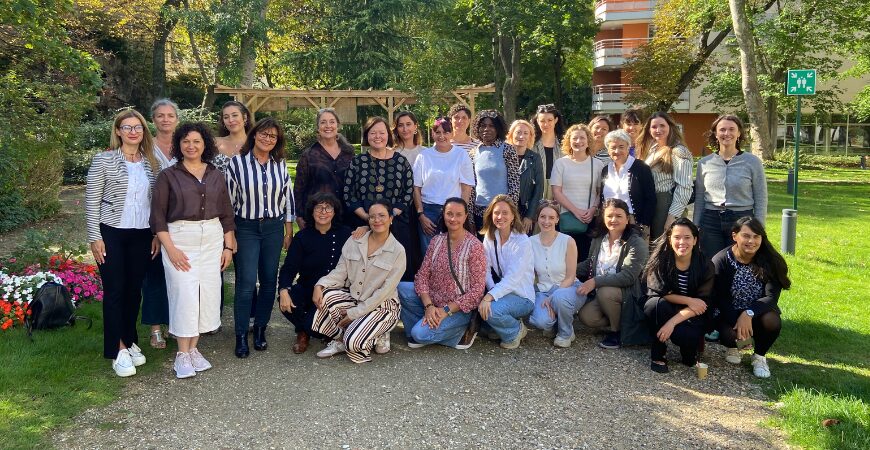
Female leadership – feedback from the pilot programme
In September 2025, Emmaus Europe launched a brand-new initiative: the first edition of the Women’s Leadership Programme. (more…)
Food is a Human Right for All European Citizens
Emmaus Europe has joined the European Citizens’ Initiative “Food is a Human Right for All!”. The signature collection has officially opened on 7 January.
(more…)
Healing Trauma: Emmaus Norfolk & Waveney’s Pioneering Women’s Project
According to a study carried out by Fobbed Off, in 2021 60% of homeless adults living in temporary accommodation in England were women.
(more…)